Practical Grammar 13: Difference between revisions
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
[[ File:Rain-AgrSJPG.JPG | 100px]] | [[ File:Rain-AgrSJPG.JPG | 100px]] | ||
As (1) shows, weather verbs demand the meaningless form ''it'' as their SUBJ. Such meaningless words are called '''expletives'''. | As (1) shows, weather verbs demand the meaningless form ''it'' as their SUBJ. Such meaningless words are called '''expletives'''. Thus, English has both an expletive ''it' (= meaningless) and a referential ''it' (a third person singular pronoun, as in ''I saw it''. | ||
== Existential sentences == | == Existential sentences == | ||
Revision as of 09:36, 5 February 2021
When it rains, it pours
Implement the analysis of weather verbs that is given on p. 107 of the textbook. Your grammar should predict the following facts:
(1) It rained.
(2) *Ingrid rained
For (1), your grammar should produce the Argument Structure below as the only grammatical output:
As (1) shows, weather verbs demand the meaningless form it as their SUBJ. Such meaningless words are called expletives. Thus, English has both an expletive it' (= meaningless) and a referential it' (a third person singular pronoun, as in I saw it.
Existential sentences
English has a second expletive, namely the word there in sentences like (3):
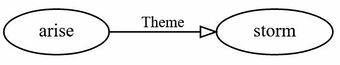
(3) There arose a storm
These sentences are called existential sentences, because they express that an instance of the concept named by the postverbal NP exists or comes about. Sentence (3), for instance, says that a storm came into existence. This can also be expressed by "A storm arose", but (3) stresses the existential change more.
Existential sentences require the expletive "there" as a SUBJ, because the existance is expressed by the verb arise and there contributes no meaning to the sentence. In this usage, there' is a noun.
From what was said above, the constrast between (3) and (4) follows. Implement these two sentences:
(4) *Ingrid arose a storm
Sentence (3) should get a single Argument Structure, namely the following one:
Weather verbs and existential verbs in functional control constructions
Now, we are going to test whether your solution to the exercise in Unit 9 and your solutions to the two problems above work together correctly.
Add the following test items to your grammar and parse all items:
(5) *There bought olives
(6) *Ingrid rained
(7) *There rained
(8) *Ingrid arose a storm
(9) *It arose a storm
(10) *It tried to rain
(11) *There tried to arise a storm
(12) It seemed to rain
(13) There seemed to arise a storm
The data above together with the data from Unit 9 illustrate the following generalizations:
a. The verb buy tolerates as its SUBJ the word Ingrid but not the words it and there.
b. The verb rain tolerates as its SUBJ the word it but not the words Ingrid and there.
c. The verb arise in its existential use tolerates as its SUBJ the word there but not the words Ingrid and it.
d. The verb buy can serve as the head of the complement of the raising verb seem, but the verbs rain and arise cannot.
e. All three verbs buy, rain and arise can serve as the head of the complement of the control verb try.