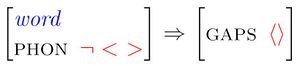Syntax 1 Wiki: Week 8: Difference between revisions
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
Exercise | |||
* Go to the [http://141.2.159.95:7002/wt/ Online Grammar 2] with the gap above. | |||
* Parse the following strings: | |||
** him Lilly likes (choose solution 1) | |||
** him Lilly spoke to (choose solution 3) | |||
** to him Lilly spoke (choose solution 4) | |||
* Parse the following strings: | |||
** he Lilly likes (choose solution 1) | |||
** he Lilly spoke to (choose solution 1) | |||
** Lilly gave the apple to him | |||
** to him Lilly gave the apple (choose solution 4) | |||
** Lilly gave the apple at him | |||
** at him Lilly gave the apple (choose solution 4) | |||
<span style="color: blue>'''Exercise:'''</span> | |||
* Parse all the sentences below and see whether you find a pattern in the data: | |||
(1) <br> | |||
a. Lilly likes Fido.<br> | |||
b. Fido, Lilly likes __. | |||
(2) <br> | |||
a. Lilly depends on Fido.<br> | |||
b. Fido, Lilly depends on __. | |||
(3) <br> | |||
a. Lilly depends on Fido.<br> | |||
b. On Fido, Lilly depends __. | |||
(4) <br> | |||
a. Lilly is fond of Fido.<br> | |||
b. Fido, Lilly is fond of __. | |||
(5) <br> | |||
a. Lilly showed me a picture of Fido.<br> | |||
b. Fido, Lilly showed me a picture of __. | |||
(6) <br> | |||
a. Lilly said I like Fido.<br> | |||
b. Fido, Lilly said I like __. | |||
(7) <br> | |||
a. Lilly said I claimed she likes Fido.<br> | |||
b. Fido, Lilly said I claimed she likes __. | |||
Because preposing can in principle span arbitrarily many clauses, it is one example of a long distance dependency! | |||
(8) * Fido, Lilly smokes __.<br> | |||
(9) * To Fido, Lilly likes __.<br> | |||
(10) * She, Lilly likes __.<br> | |||
(11) * To Fido, Lilly depends __.<br> | |||
(12) * Fido, Lilly claims __ am sad.<br> | |||
(1) <span style="color: blue>What pattern do (1)-(12) show?</span> | |||
<div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:800px"> | |||
Check your answer | |||
<div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | |||
An expression can be preposed from a position P if and only if it can occur in position P. | |||
</div> | |||
</div><br> | |||
Revision as of 18:57, 10 December 2020
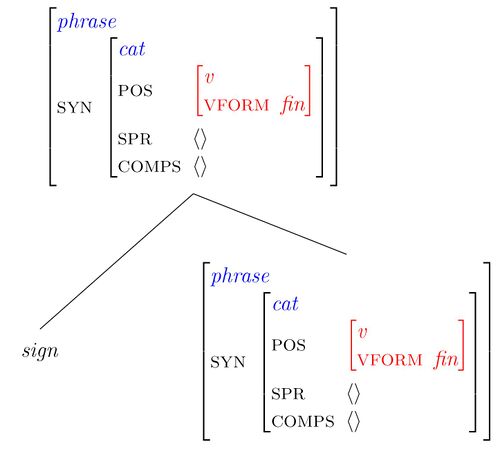
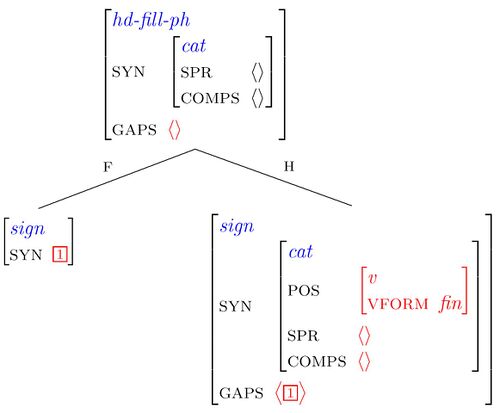
Step 2 Licensing the extra expression at the beginning of the sentence
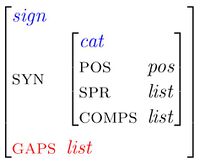
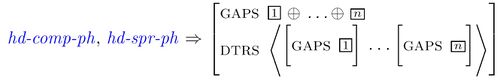
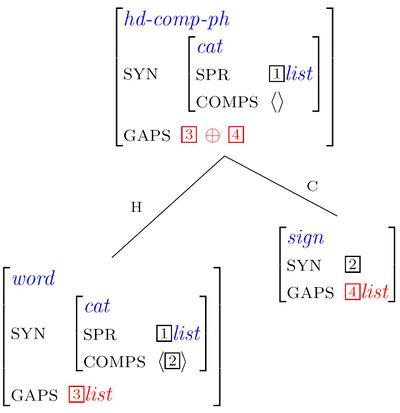
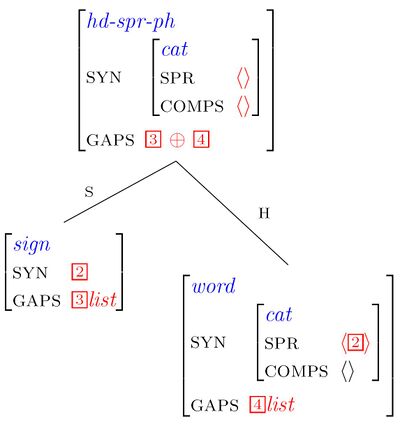
Introducing the GAPS feature
The Gap Collection Constraint
Illustrating the Gap Collection Constraint
The Head-filler schema
Exercise
- Go to the Online Grammar 2 with the gap above.
- Parse the following strings:
- him Lilly likes (choose solution 1)
- him Lilly spoke to (choose solution 3)
- to him Lilly spoke (choose solution 4)
- Parse the following strings:
- he Lilly likes (choose solution 1)
- he Lilly spoke to (choose solution 1)
- Lilly gave the apple to him
- to him Lilly gave the apple (choose solution 4)
- Lilly gave the apple at him
- at him Lilly gave the apple (choose solution 4)
Exercise:
- Parse all the sentences below and see whether you find a pattern in the data:
(1)
a. Lilly likes Fido.
b. Fido, Lilly likes __.
(2)
a. Lilly depends on Fido.
b. Fido, Lilly depends on __.
(3)
a. Lilly depends on Fido.
b. On Fido, Lilly depends __.
(4)
a. Lilly is fond of Fido.
b. Fido, Lilly is fond of __.
(5)
a. Lilly showed me a picture of Fido.
b. Fido, Lilly showed me a picture of __.
(6)
a. Lilly said I like Fido.
b. Fido, Lilly said I like __.
(7)
a. Lilly said I claimed she likes Fido.
b. Fido, Lilly said I claimed she likes __.
Because preposing can in principle span arbitrarily many clauses, it is one example of a long distance dependency!
(8) * Fido, Lilly smokes __.
(9) * To Fido, Lilly likes __.
(10) * She, Lilly likes __.
(11) * To Fido, Lilly depends __.
(12) * Fido, Lilly claims __ am sad.
(1) What pattern do (1)-(12) show?
Check your answer
An expression can be preposed from a position P if and only if it can occur in position P.
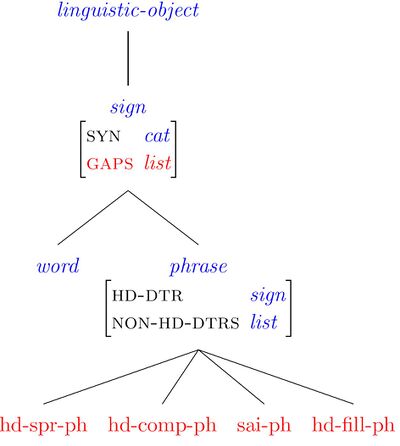
We distinguish between two kinds of phrases:
1. Stand(ard) phrases: hd-comp-ph, hd-spr-ph, hd-c-ph, sai-ph
2. Head-Filler phrases: top-ph, question
Remarks:
1. ⊕ is the list merger operator. (to merge = verschmelzen)
2. L1 ⊕ L2 is the new list L3 which contains all the elements of list L1 followed by all the elements of list L2.
Examples:
1. <> ⊕ < a > = < a >
2. < a > ⊕ <> = < a >
3. < a, a > ⊕ < a, b, c > = < a, a, a, b, c >