Syntax 1 Wiki: Week 6: Difference between revisions
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
===Head-Modifier Phrases=== | ===Head-Modifier Phrases=== | ||
There are 3 kinds of head-modifier phrases.<br> | There are 3 kinds of head-modifier phrases.<br> | ||
Scheme 1. A Head-modifier phrase can be formed by combining <i style="color:blue;">an adjectival sign</i> [= the non-head | |||
daughter] with <i style="color:blue;">a nominal sign</i> [= the head daughter] which is COMPS-complete but is sill looking | daughter] with <i style="color:blue;">a nominal sign</i> [= the head daughter] which is COMPS-complete but is sill looking | ||
for its specifier. | for its specifier. | ||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Scheme 2. A Head-modifier phrase can be formed by combining <i style="color:blue;">a nominal sign</i> [= the head daughter]which is COMPS-complete but is sill looking for its specifier with <i style="color:blue;">a PP</i> [= the non-head daughter] | |||
[[File:H-M phrase 2.PNG|left|400px|caption]] | [[File:H-M phrase 2.PNG|left|400px|caption]] | ||
<div style="color:#fff; background:#72777d"> | <div style="color:#fff; background:#72777d"> | ||
| Line 103: | Line 103: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Scheme 3. A Head-modifier phrase can be formed by combining <i style="color:blue;">a verbal sign</i> [= the head daughter] which is COMPS-complete but is sill looking for its specifier with <i style="color:blue;">a PP</i> [= the non-head daughter]. | |||
[[File:H-M phrase 3.PNG|left|400px|caption]] | [[File:H-M phrase 3.PNG|left|400px|caption]] | ||
<div style="color:#fff; background:#72777d"> | <div style="color:#fff; background:#72777d"> | ||
Revision as of 13:15, 1 July 2019
Types of Phrases
Head-Complement Phrases
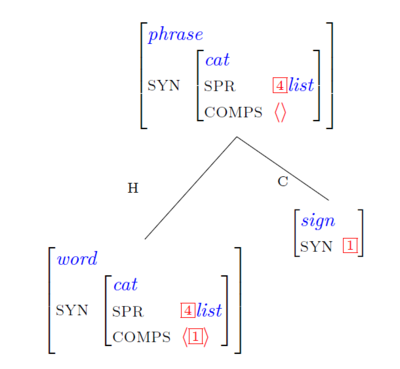
A head-complement phrase can be formed by combining a word [= the head daughter] with 1 or 2 signs [= the non-head daughter(s)] whose syntactic categories can be unified with the syntactic categories on the word’s comps list.
Scheme 1: The head licenses 1 complement
This schema licenses the following structure:
XP -> X + COMPS
Examples:
- [PP [H of][C Lilly]]
- [AP [H fond][C of Lilly]]
- [VP [H likes][C Fido]]
- [VP [H speaks][C to Fido]]
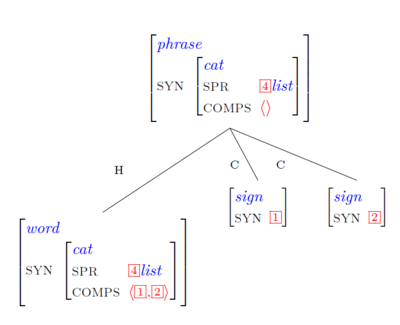
Scheme 2: The head licenses 2 complements
This schema licenses the following structures:
VP -> V N(P) N(P)
VP -> V N(P) PP
Examples:
- [VP [H show][C me][C Frankfurt]]
- [VP [H give][C the book][C to the student]]
- [VP [H put][C the book][C on the table]]
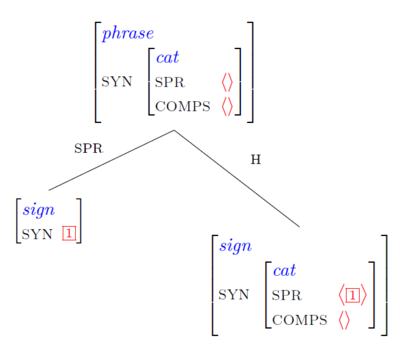
Head-Specifier Phrases
A head-specifier phrase can be formed by combining a sign [= the head daughter] with a second sign [= the non-head daughter] whose syntactic category can be unified with the syntactic category on the word’s spr list:
This schema licenses the following structures:
- NP -> D N(P)
- [NP [SPR the][H student]]
- [NP [SPR those][H apples]]
- S -> N(P) V(P)
- [S [SPR Lilly][H smokes]]
- [S [SPR Lilly][H likes Fido]]
- [S [SPR The student][H showed a cat to Fido]]
Head-Modifier Phrases
There are 3 kinds of head-modifier phrases.
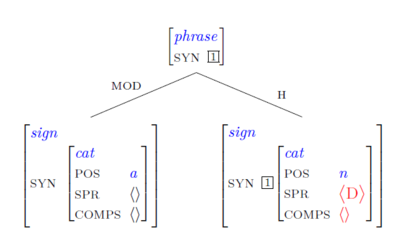
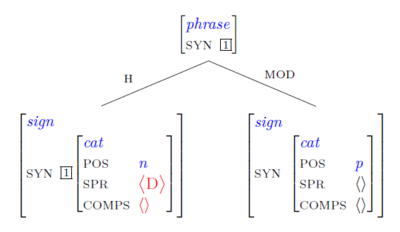
Scheme 1. A Head-modifier phrase can be formed by combining an adjectival sign [= the non-head
daughter] with a nominal sign [= the head daughter] which is COMPS-complete but is sill looking
for its specifier.
This schema licenses the following structure:
- NP -> A N(P)
- [NP [MOD happy][H student]]
- [NP [MOD big][H cat]]
- [NP [MOD huge][H interest in languages]]
Scheme 2. A Head-modifier phrase can be formed by combining a nominal sign [= the head daughter]which is COMPS-complete but is sill looking for its specifier with a PP [= the non-head daughter]
This schema licenses the following structure:
- NP -> N(P) PP
- [NP [H student][MOD with red hair]]
- [NP [H professor][MOD from Frankfurt]]
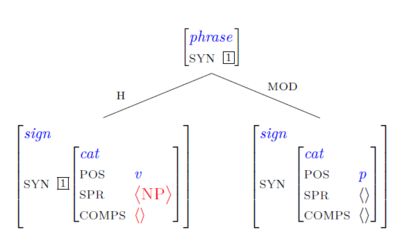
Scheme 3. A Head-modifier phrase can be formed by combining a verbal sign [= the head daughter] which is COMPS-complete but is sill looking for its specifier with a PP [= the non-head daughter].
This schema licenses the following structure:
- VP -> V(P) PP
- [VP [H works][MOD at the university]]
- [VP [H saw Lilly][MOD with a cat]]
Phrase Formation
Navigation: