Semantics 2: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
! Header text !! Header text !! Header text | ! Header text !! Header text !! Header text | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Z<sup>1</sup>|| Example || Example | | Z<sup>1</sup> = _is an element<br>|| Example || Example | ||
|- | |- | ||
| A<sup>1</sup> = _is a circle<br>|| Example || Example | | A<sup>1</sup> = _is a circle<br>|| Example || Example | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
|} | |} | ||
<!-- | |||
Key: | Key: | ||
| Line 42: | Line 43: | ||
T<sup>2</sup> = _is directly to the right of _<br> | T<sup>2</sup> = _is directly to the right of _<br> | ||
W<sup>3</sup> = _is directly between _ and _<br> | W<sup>3</sup> = _is directly between _ and _<br> | ||
--> | |||
Name = {a, b, c, d, e, f}<br> | Name = {a, b, c, d, e, f}<br> | ||
Revision as of 19:24, 21 January 2021
| Header text | Header text | Header text |
|---|---|---|
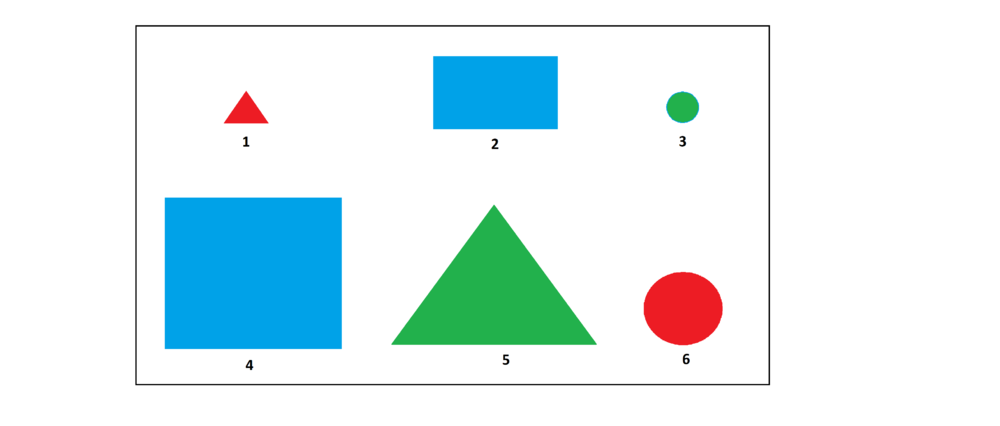
| Z1 = _is an element |
Example | Example |
| A1 = _is a circle |
Example | Example |
| B1 = _is a triangle |
Example | Example |
| C1 = _is a square |
Example | Example |
| D1 = _is green |
Example | Example |
| E1 = _is red |
Example | Example |
| G1 = _is blue |
Example | Example |
Name = {a, b, c, d, e, f}
Const = {A, B, C, D, E, G, H, J, K, L N, O, P, Q, R S, T, W}
M = <U, F> such that
U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
F(a) = 1
F(b) = 2
F(c) = 3
F(d) = 4
F(e) = 5
F(f) = 6