User:Gert
Semantic analysis of sentences into predicates and arguments
Note: Many of the sentences in this section are taken from or based on examples in Hornby, A.S. (1975) Guide to Patterns and Usage in English. Second Edition. Cornelsen & Oxford University Press.
Establishing the head of a phrase
Establish what phrase the words below form and identify the head of the phrase!
Valence
2. Kim needs new shoes. 3. Kim talked to the student. 4. Kim sent the student to Robin. 5. Kim lent Robin a bicycle. 6. Kim told Robin that the student likes her. 7. Kim suggested to Robin that the student likes her. 8. Kim wants [to eat an apple.] 9. Kim believes Robin to like the student. 10. Kim seems to like the student. 11. Kim is intelligent. 12. Kim found the movie interesting. 13. Kim talked to Robin about the student. 14. Kim saw Robin talk to the student. 15. The student amuses Kim. 16. Kim came out of the room.
Words
| Verb | SUBJ | COMPS |
|---|---|---|
| snore | <NP> | <> |
| own | <NP> | <NP> |
| put | <NP> | <NP,NP> |
Verb SUBJ COMPS
snore <NP> <> own <NP> <NP> put <NP> <NP,PP>
When you look up the word scissors in the Oxford Learner's Dictionary, you are given the following information about it:
| Phonology | scissors |
| Part of speech | noun |
| Number | plural |
| Content | a tool for cutting paper ... |
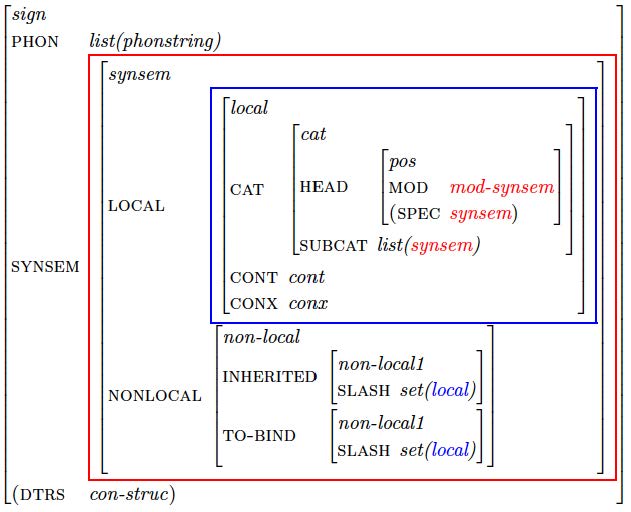
The following representation shows how we will structure the information in a word in this course:
http://www.ello.uos.de/field.php/Syntax/Syntax
A video on the concept grammar
<iframe width="420" height="315"
src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/JRiX8Jiq_Z4">
</iframe>