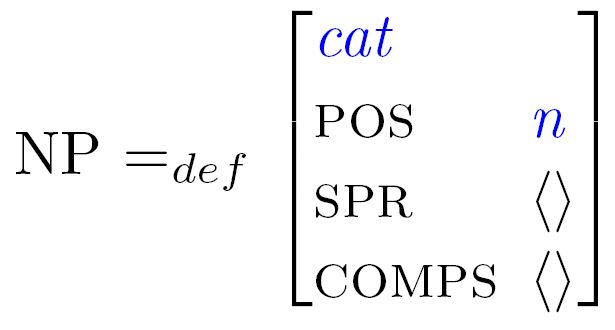Syntax 1 Wiki: Week 6
Abbreviations
To make life easier on us, we use a number of abbreviations in valence lists, e.g. NP, PP, etc. In the next exercise you are supposed to find out which feature structures each of these abbreviations stand for. To this end, do the following exercises.
- Go to the online grammar.
- Click on the lexical entry for amuse.
- Click on the tree.
- There are two NP-nodes in the verb's valence lists.
- Open both of them and find what the two feature structures have in common. That is what the symbol "NP" abbreviates.
Exercises
(1) Which feature structure does the symbol "NP" stand for?
Auxiliaries
Raising
- There is a special verb class called subject raising verbs.
- These verbs are easy to identify by applying the following tests.
- If the verb passes theses tests, then it is a subject raising verbs.
- Usually, if the verb passes one of these tests, then it passes all of them.
Subject raising verb Test Nr. 1
If the verb V takes a non-finite VP-complement headed by the verb rain, then V must take the idiomatic word it as its subject.
Illustration:
(1)
a. Itidiom rained.
b. Itidiom will rain.
(2)
a. * The student rained.
b. * The student will rain.
Subject raising verb Test Nr. 2
If the verb V takes a non-finite VP-complement headed by a verb that selects an idiomatic NP as its subject, then V must take this idiomatic NP as V’s subject.
Illustration:
(1)
a. All hellidiom brokeidiom loose.
b. All hellidiom will breakidiom loose.
(2)
a. * An accidentidiom brokeidiom loose.
b. * An accidentidiom will breakidiom loose.
Subject raising verb Test Nr. 3
If the verb V takes a non-finite VP-complement headed by a verb that imposes semantic requirements on its subject, then V must impose those same semantic requirements on V’s subject. Illustration:
The verb kill only requires of its subject that it express some kind of force that kills the referent of the direct object. That force can be alive or not:
(3)
a. The student willV kill the politician.
b. The accident willV kill the politician.
In contrast, the verb assassinate requires its subject to express a person. Forces cannot assassinate anyone!
(4)
a. The student willV assassinate the politician.
b. * The accident willV assassinate the politician.
The same case can be made with the verbs like (which requires a living being as its subject) or happen (which requires an event as its subject).
Subject raising verb Test Nr. 4
If the verb V takes a non-finite VP-complement headed by a verb that selects a subject of a particular syntactic category, then V must select a subject of the same syntactic category.
Illustration:
The verb like requires its subject to be an NP:
(5)
a. [NP The student] willV like the politician.
b. * [S That the student smokes] willV like the politician.
In contrast, the verb annoy allows its subject to be an NP or an S:
(6)
a. [NP The student] willV annoy the politician.
b. [S That the student smokes] willV annoy the politician.
The student
Navigation: